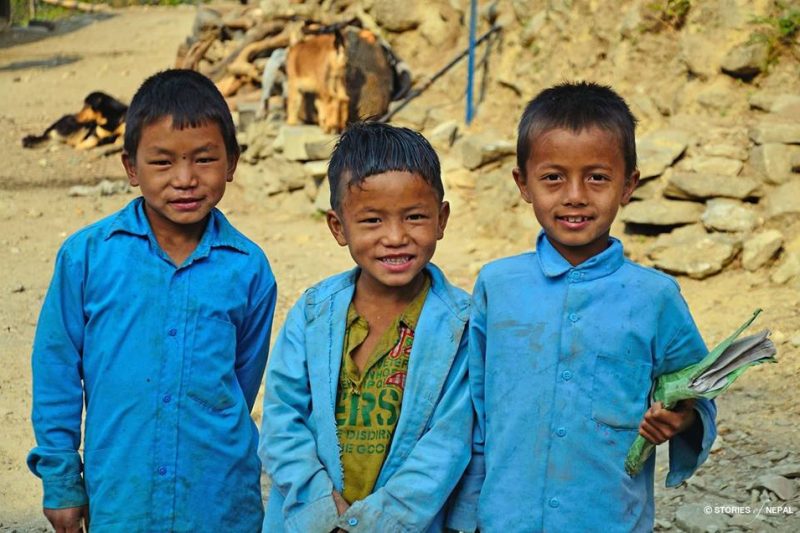
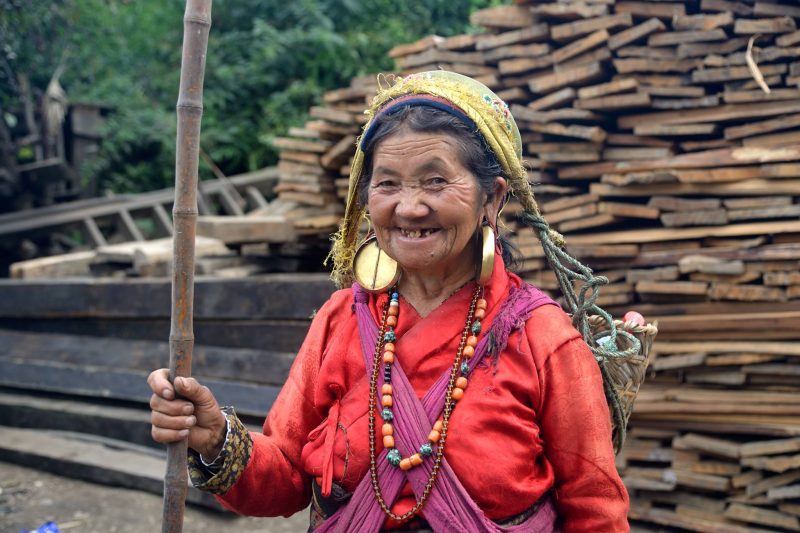
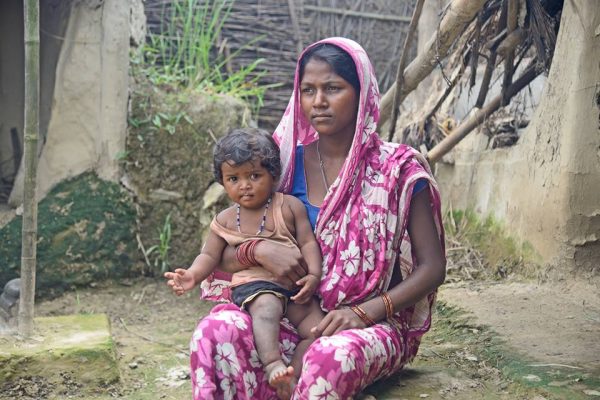
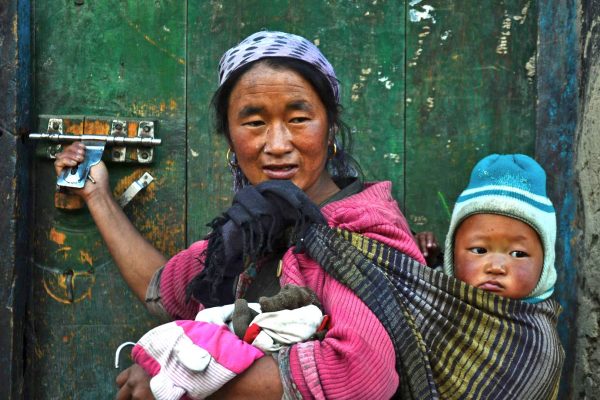
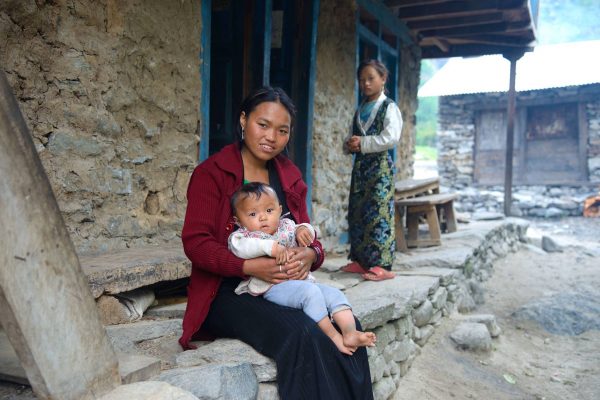
Nepal is a landlocked sovereign country, located in Southern Asia between China in north and India in the south. It is among the poorest and least developed countries in the world, with almost one- quarter of its population living below the poverty line. Nepal’s ecological zones run east to west about 800 km along its Himalayan axis, 150 to 250 km north to south. The country is divided into three main geographical regions: the Himalayan region, the mid-hill region and the Terai (plain) region. The highest point in the country is Mt. Everest (8,848 m)—which is also the highest peak in the world—whereas the lowest point is in Kechana Kalan in Jhapa (60 m). Agriculture is mainstay of the economy, providing a livelihood of three- fourth of the population and accounting for about one-third of GDP (source: CIA World fact book 2011).Industrial activity mainly involves the processing of agricultural products, including pulses, jute, sugarcane, tobacco, and grain. The major source of foreign currency is tourism industry. More than 40 caste/ethnic groups are accommodated in the country and there are about 70 spoken languages in Nepal. The overall literacy rate (for population age 5 years and above) increased from 54.1% in 2001 to 65.9% in 2011. The male literacy rate was 75.1% compared to the female literacy rate of 57.4%.
A “ People’s War”, started in February 1996 by the Communist Party of Nepal (Maoist). The Communist Party of Nepal started a violent bid to replace the royal parliamentary system with a people’s republic. This led to the long Nepali Civil War and more than 12,000 deaths .The worst affected in this conflict were the children .According to UNICEF, over 40,000 children in Nepal are estimated to have been displaced over the course of Maoist uprising (source: UN chronicle, 2006). Nepal’s decade-long armed conflict ended 2006 with the signing of the Comprehensive Peace Accord (CPA) between the Government and the Communist Party of Nepal (Maoist). A central pillar of the accord was the writing of a new constitution that would grant equal rights and opportunities to all Nepalese people. The constitution came into effect on 20 September 2015, replacing the Interim Constitution of 2007.
The April 2015 Nepal earthquake killed nearly 9,000 people and injured nearly 22,000. Hundreds of thousands of people were made homeless, children displaced and orphaned, with entire villages flattened across many districts of the country. Centuries-old buildings were destroyed at UNESCO World Heritage Sites in the Kathmandu Valley.